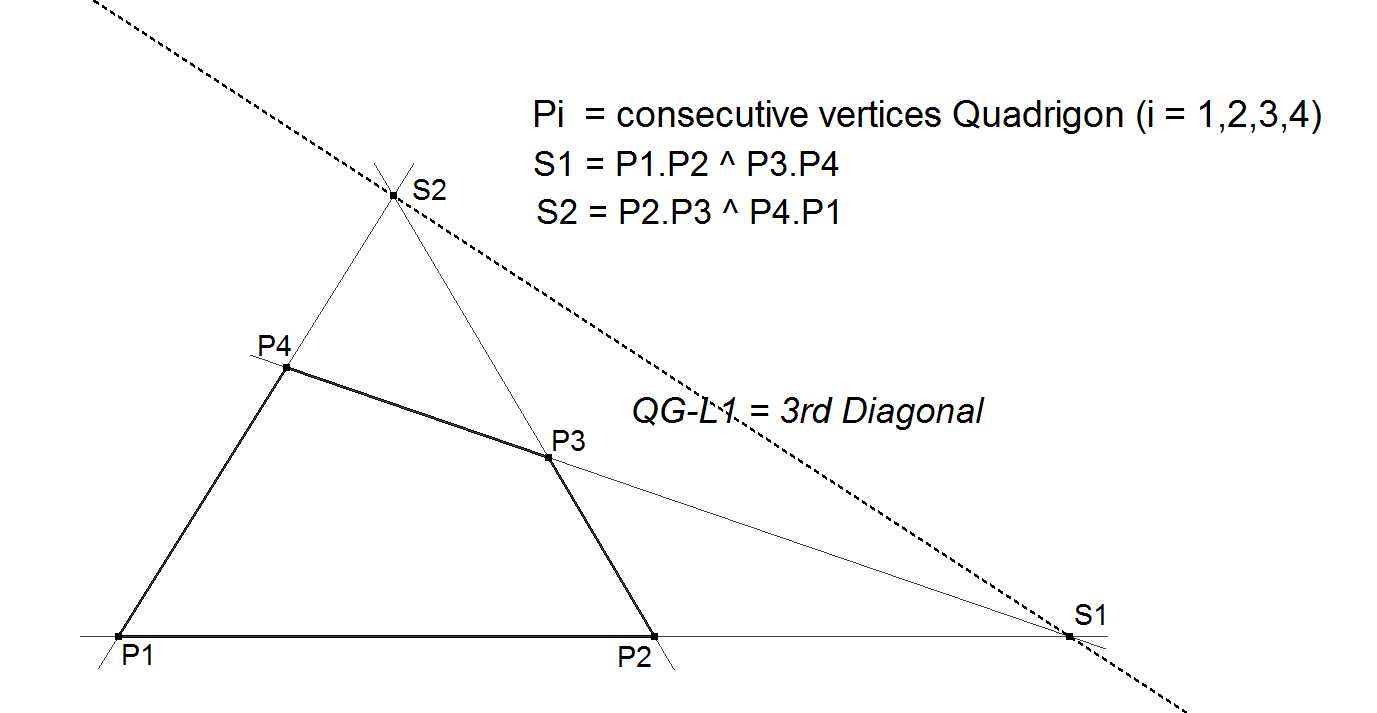
QG-L1: The 3rd diagonal
The 3rd diagonal of a Quadrigon is the connecting line of S1 and S2, where S1 and S2 are the intersection points of the opposite sides of the Reference Quadrigon.
CT-Coefficients QG-L1 in 3 QA-Quadrigons
(-q r : p r : p q)
(q r : -p r : p q)
(q r : p r : -p q)
CT-Coefficients QG-L1 in 3 QL-Quadrigons
(0 : m : n)
( l : 0 : n)
( l : m : 0)
DT-Coefficients QG-L1 in 3 QA-Quadrigons
(0 : 1 : 0)
(1 : 0 : 0)
(0 : 0 : 1)
DT-Coefficients QG-L1 in 3 QL-Quadrigons
(0 : 1 : 0)
(1 : 0 : 0)
(0 : 0 : 1)
Properties
- These points lie on QG-L1: QG-P2, QG-P3, QG-P17, QG-2P2a, QG-2P2b, QG-3Pa, QG=3Pb.
- The three 3rd Diagonals in the QA-environment form the QA-Diagonal Triangle.
- The three 3rd Diagonals in the QL-environment form the QL-Diagonal Triangle.
- QG-L1 (see [13], Polar) is the polar of any inscribed QG-conic.
- QG-L1 (see [13], Polar) is the polar of any circumscribed QG-conic.
- QG-L1 is the QL-Tf1 image of the circle QG-Ci3.
Estimated human page views: 637