QG-2P2: Endpoints 3rd QA-diagonal
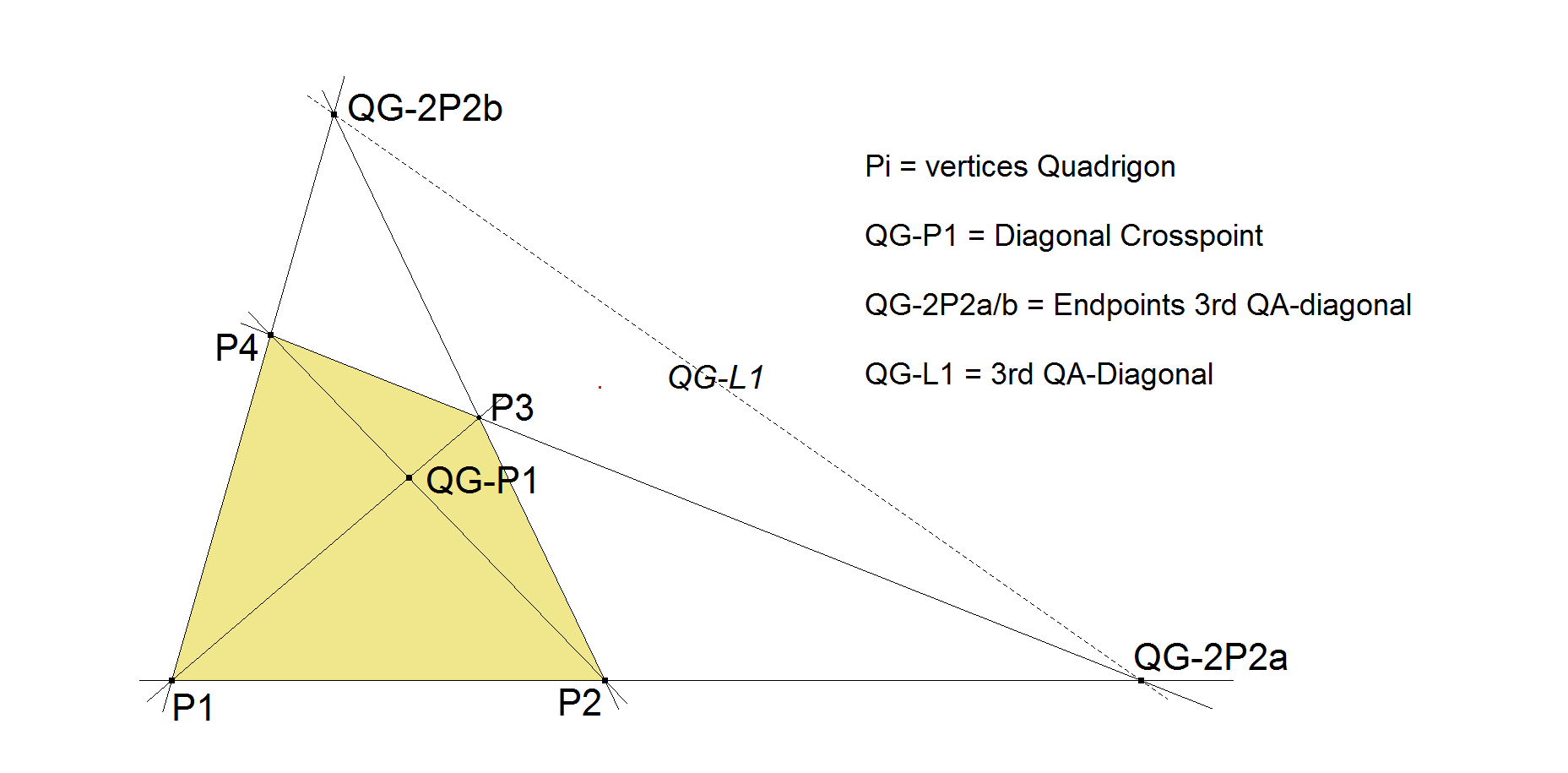
In a Quadrigon (system of 4 consecutive points P1, P2, P3, P4) the Diagonal Triangle of a Quadrangle (system of 4 points unrestricted) can be seen as a triangle with these vertices:
- the Diagonal Crosspoint (QG-P1) representing the 1st vertex,
- the Endpoints at the QA-3rd Diagonal representing the 2nd and 3rd vertice, which are QG-2P2a and QG-2P2b.
When the Quadrigon vertices are P1, P2, P3, P4 in this order, then:
- QG-P1 = intersection point P1.P3 ^ P2.P4
- QG-2P2a = intersection point P1.P2 ^ P3.P4
- QG-2P2b = intersection point P1.P4 ^ P2.P3.
CT-coordinates QG-2P2a/b in 1st QA-Quadrigon:
QG-2P2a:(p : q : 0)
QG-2P2b: (0 : q : r)
CT-coordinates QG-2P2a/b in 1st QL-Quadrigon:
QG-2P2a:(0 : 1 : 0)
QG-2P2b: (n : 0 : -l)
DT-coordinates QG-2P2a/b in 1st QA-Quadrigon:
QG-2P2a:(0 : 0 : 1)
QG-2P2b: (1 : 0 : 0)
DT-coordinates QG-2P2a/b in 1st QL-Quadrigon:
QG-2P2a:(n : 0 : l)
QG-2P2b: (n : 0 : -l)
Properties
- QG-2P2a and QG-2P2b are collinear with QG-P2, QG-P3, QG-2P3a/b.
- QG-2P2a and QG-2P2b are each other’s Reflection in QG-P2.
- QG-2P2a and QG-2P2b define the line segment which is the diameter of QG-Ci1 (QA-DT-Thales Circle).
- Let L2a and L2b be the lines through QG-2P2a and QG-2P2b parallel to QG-P1.QL-P13. Let L3a, L3b and L3c be the sidelines of the QL-Diagonal Triangle, L3c being the 3rd diagonal QG-L1. The pairs of triangles (L3a,L3c,L2a) and (L3b,L3c,L2a) as well as (L3a,L3c,L2b) and (L3b,L3c,L2b) have equal areas. See [50], ADGEOM #2380/2382/2383, where L2a and L2b are called area equalizers.
Estimated human page views: 686